Understanding Your Air Conditioning System
1. Key Components of Air Conditioning
Air conditioning systems are complex setups designed to create a comfortable indoor environment, particularly during the hot summer months. They operate through the collaboration of several essential components, including:
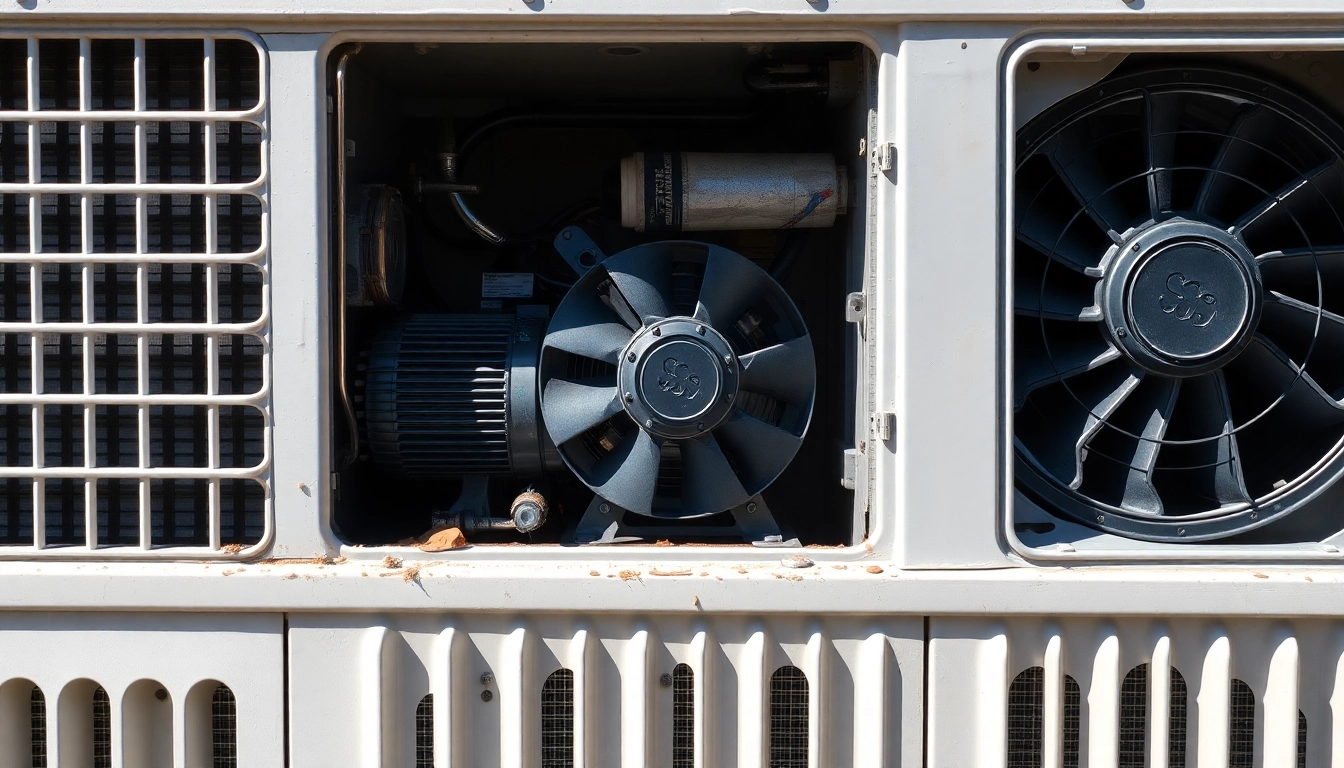
- Compressor: Often considered the heart of the system, the compressor pumps refrigerant through the system, absorbing heat from the indoor air and releasing it outside.
- Evaporator Coils: Located inside your home, the evaporator coils absorb heat from the indoor air, causing the refrigerant inside to evaporate and cool the surrounding air.
- Condenser Coils: These coils, found outside the home, expel the absorbed heat from the refrigerant to the outside air, causing the refrigerant to condense back into a liquid state.
- Air Handler: The air handler circulates the cooled air throughout the home via ductwork.
- Thermostat: This device regulates the temperature by controlling when the air conditioning system turns on and off.
2. How Air Flow Works in HVAC Systems
The efficiency of your air conditioning system heavily relies on the airflow. Air needs to move freely throughout the system to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. Airflow is facilitated through a network of ductwork, vents, and the air handler. Here’s how it works:
- The thermostat detects when the temperature rises above the set point and signals the air conditioning system to turn on.
- The compressor engages, and the refrigerant circulates through the system, drawing heat from the indoor air.
- The air handler pushes the cooled air through the ductwork and into various rooms through the vents.
When any of these components encounter an issue, such as increased resistance due to blockages or improperly functioning parts, airflow can be disrupted, leading to problems like poor cooling or an air conditioning not blowing cold air at all.
3. Importance of Regular Maintenance
Routine maintenance of your air conditioning system is crucial for optimal performance. Energy costs can skyrocket if your system is not running efficiently. Regular check-ups can identify minor issues before they become major problems, thereby extending the lifespan of your system. Here are a few critical maintenance tasks:
- Changing or cleaning air filters regularly to prevent airflow restrictions.
- Checking refrigerant levels to ensure efficient heat absorption.
- Inspecting ductwork for leaks that can diminish system efficiency.
- Cleaning condenser coils to enhance heat rejection capability.
Identifying Issues When Air Conditioning is Not Blowing
1. Signs Your AC is Not Functioning Properly
Recognizing the warning signs of an underperforming air conditioning system can make a significant difference in addressing problems early. Here are some signs to watch out for:
- Inconsistent temperatures throughout your home.
- Unusual noises such as rattling or grinding sounds when the AC is running.
- Increasing energy bills without an apparent reason, indicating potential inefficiency.
- Humidity levels indoors feeling higher than normal.
2. Common Symptoms of Airflow Problems
When airflow is compromised, you may experience:
- No air or very little air blowing from vents, even when the system is running.
- Warm air instead of cool air when the AC is on.
- Extended run times preparing to achieve the desired temperatures.
3. Importance of Timely Diagnosis
Delaying the diagnosis of air conditioning issues can lead to more severe problems and costly repairs. For instance, a minor blockage in the ductwork could lead to frozen coils if not addressed promptly, resulting in significant downtime for your AC unit and higher repair costs. Ensuring you identify the problem while it is still manageable can save both time and money.
Common Causes of Air Conditioning Not Blowing
1. Clogged Air Filters
One of the most common reasons why an air conditioning system does not blow air effectively is clogged air filters. Dust, allergens, and debris accumulate over time in the filter, restricting airflow and causing the system to work harder. Here’s what happens:
- Air cannot flow freely through the system, leading to reduced cooling efficiency.
- The AC may freeze up, causing further complications that require professional assistance.
To prevent this, check the air filters monthly (especially during high usage months) and replace or clean them when they become dirty.
2. Broken Blower Motor
The blower motor is crucial for moving air through the ducts. If the motor fails, it can cause the entire system to stop blowing air. Symptoms of a malfunctioning motor include:
- The AC unit runs, but no cool air is produced.
- Unusual sounds that may indicate motor struggle, such as buzzing or screeching.
- Failure of the air handler to start even when the system is activated.
If this is suspected, hiring a professional HVAC technician to assess the motor is recommended.
3. Frozen Evaporator Coils
Frozen evaporator coils can severely hinder airflow and may indicate an underlying problem. Causes for coil freezing include:
- Insufficient airflow due to clogged filters or blocked ducts.
- Low refrigerant levels which can be caused by leaks or improper installation.
- High humidity levels in the environment causing the coils to freeze over.
When coils freeze, it’s essential to turn off the AC immediately and allow them to thaw before considering further troubleshooting. Continuing to operate the system could lead to catastrophic failure and costly repairs.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
1. How to Check Your AC Settings
Sometimes, the simplest issues relate to the thermostat settings. Here’s a quick guide to ensure your settings are correct:
- Check if the thermostat is set to ‘Cool’ mode.
- Ensure the temperature setting is lower than the current indoor temperature.
- Look for any display issues or indication lights that may signal problems.
If all settings seem correct, move on to other potential issues.
2. Inspecting and Replacing Air Filters
Always start with an inspection of the air filters. Here’s how to do it:
- Turn off the power to the AC unit for safety.
- Remove the air filter and check for dirt accumulation. If it appears dirty, it needs to be replaced.
- Replace the filter with a new one or clean it depending on your system’s requirements.
- Reinstall the filter and turn the system back on to see if airflow improves.
3. When to Call a Professional
If you’ve gone through troubleshooting steps and the system still isn’t blowing air, it’s time to contact a professional HVAC technician. Signs that you should seek expert help include:
- Inability to identify the problem after basic troubleshooting.
- Frequent cycling of the system which might indicate other issues.
- Presence of a strange or strong odor when the system is running.
Professional technicians have the expertise and tools to diagnose and resolve complex issues efficiently.
Preventative Measures for Airflow Issues
1. Scheduling Regular Maintenance Checks
Establishing a routine maintenance schedule can dramatically improve the longevity and efficiency of your air conditioning system. Consider scheduling maintenance checks at least twice a year, ideally once in the spring and once in the fall, to ensure smooth operation as the seasons change. Key tasks performed during these checks typically include:
- Thorough cleaning of evaporator and condenser coils.
- Checking refrigerant levels and recharging if necessary.
- Inspecting and sealing ductwork to prevent air leaks.
2. Keeping Ducts Clear and Clean
Regularly inspect and clean your ductwork, as dust and debris can restrict airflow. Consider implementing the following practices:
- Sealing any visible gaps in the ductwork to prevent air loss.
- Having a professional HVAC service perform periodic duct cleanings.
- Ensure vents are not blocked by furniture, curtains, or other objects to maintain unobstructed airflow throughout your home.
3. Using Quality Filters for Optimal Airflow
Not all air filters are created equal. Using high-quality, MERV-rated filters can significantly improve your system’s efficiency and air quality. Here are a few tips:
- Select filters that fit your specific system and environment. Higher-rated filters may capture smaller particles, improving your indoor air quality.
- Change filters regularly, typically every 1-3 months depending on usage and filter type.
- Consider a programmable thermostat that reminds you to replace your filters based on usage patterns.